Industry News
· Federal Limits on Hexavalent Chromium in drinking water are likely within three years
· EPA’s Environmental Technology Verification (ETV) Program Solicits Technology Vendors
· Critical Process Filtration, Inc. Tests Self-Contained System to Remove Radioactive Agents from Water in Japan
· North American Municipal Water Plants Receive Four Million Chemical Bids per Year
Conferences
· AWWA Pump and Valve Exhibitors
· Only a Few Treatment Chemicals Exhibitors
· Lots of Good Presentations
· Global Orchard Provides Continuing Calendar of Water Conferences
· Calgon Carbon Sponsors Free Sessions on Safe Water
Water Project Updates
Federal Limits on Hexavalent Chromium in Drinking Water are Likely within Three Years
EPA is finalizing a draft toxicology assessment of hexavalent chromium. But it is a long road from an assessment to enforceable regulations. The timeline is likely to be similar to that of arsenic. It took decades of review before EPA issued a rule reducing the maximum containment level (MCL) of arsenic in drinking water from 50 parts per billion to 10 ppb in January of 2001. The EPA administrator eventually signed off on the rule, setting an effective date of January 2006. The rule forced utilities to install a complicated technology to absorb arsenic and then deal with a large amount of wastewater containing very high levels of arsenic. Many smaller utilities were forced to double water prices. Approximately 1,000 utilities are not yet in compliance with the rule.
Administrator Lisa Jackson has made the chromium assessment a priority. But once the toxicology assessment is completed, issuing a new drinking water standard will take as much as three years.
EPA’s Environmental Technology Verification (ETV) Program Solicits Technology Vendors
Two Environmental Technology Verification (ETV) centers, Advanced Monitoring Systems (AMS) and Water Quality Protection (WQP), are soliciting vendors and collaborators interested in verification testing of their technologies. The AMS Center, operated by Battelle, is focused on technologies for monitoring contaminants in air, water, and soil. The contact is Ann Louise Sumner, Battelle, at 614-424-3973 or ETVAMSCenter@battelle.org The WQP Center, operated by NSF International, is focused on water protection and wet weather flow technologies, including coating materials for infrastructure rehabilitation. For a list of technology categories prioritized by this center, visit www.epa.gov/nrmrl/std/etv/vt-wqp.html.
The contact is Tom Stevens, NSF, at 734-769-5347 or stevenst@nsf.org.
Critical Process Filtration, Inc. Tests Self-Contained System to Remove Radioactive Agents from Water in Japan
Critical Process Filtration, Inc., manufacturer and supplier of process filtration products and services based in Nashua, NH, has developed a self-contained system designed to remove radioactive agents from water. The company hopes that once the testing process has been completed, the system can be used to help clean up the Fukushima Nuclear Power Plant site in Japan. Field testing of the system is currently underway in Japan. The process combines sorbtive beds with tried and tested particle removal filters for radiation remediation.
The system is made of gamma stable material to eliminate the possibility of plastic degradation due to radiation, and it can tolerate long storage periods before proper disposal without the threat of leakage.
The Critical Process system comprises a prefilter, a column of a specific clinoptilolite and a final filter. Together, they ensure particles from the bed do not escape the filter assembly. The company chose to use the clinoptilolite (a substance that absorbs or adsorbs another substance) as the device’s sorbent, based on a Department of Energy study in which Brookhaven National Laboratories participated. The study included extensive laboratory-scale testing to identify the optimum sorbent to remove radiation, using radioactive strontium-90 (SR-90) as a challenge contaminant. The clinoptilolite was identified as the optimum sorbent.
As a result of the Brookhaven study, a barrier wall of clinoptilolite is now being used to clean up radioactive groundwater at an inactivated nuclear fuel reprocessing plant in New York. It is also being used at the Chalk Hill nuclear facility in Canada. Contractors for the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) have used the same sorption technique to remove SR-90, I-129, Tc-99 and uranium from contaminated ground water at the Savannah River site in Georgia.
Critical Process says that if the radioactivity in Japan mimics that of the nuclear sites that have already benefited from its technique, the tests results should be successful. The company notes that the new device should not be run at flow rates greater than 1 liter per minute to ensure dwell times that allow for adequate removal. More accurate data on flow, removal efficiency and capacity will be available after testing is completed.
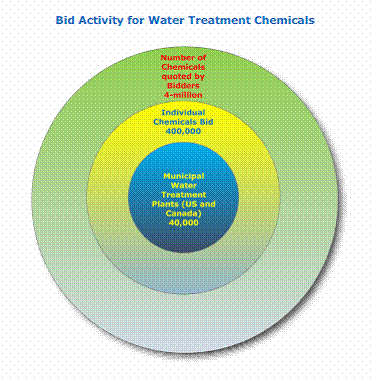
North American Municipal Water Plants Receive Four Million Chemical Bids per Year
There are more than 40,000 municipal plants purifying the drinking water for residents in Canada and the U.S. Each of them buys an average of 10 different types of chemicals yearly. Often there are dozens of bidders. This results in millions of individual bids per year by approximately 100 suppliers of these chemicals. McIlvaine tracks the activities at individual plants including expansions, equipment replacements and chemical purchases in North American Public Water Plants and People (an online service with biweekly updates). Chemicals include activated carbon, chlorine, ferric chloride, lime and many others.
Chlorine has been a major part of municipal water treatment for nearly 100 years. About 98 percent of municipal water treatment facilities now use chlorine disinfectant as their disinfectant of choice.
The selection of chemicals is now influenced by the necessity of meeting Trihalomethanes limits. Chlorine dioxide is not a chlorinating agent and can be used as a primary disinfectant or as a raw water oxidant, for THM and HAA precursor reduction in potable water treatment systems. It can also be a quick option for utilities struggling with compliance issues.
Chemicals are also used for filtration and separation processes occurring at the plant. Coagulants/flocculants include iron hydroxide, aluminum hydroxide and synthetic polymers.
In terms of annual tonnage, lime ranks first among chemicals used in the treatment of potable and industrial water supplies. Lime is used by many municipalities to improve water quality, especially for water softening and arsenic removal.

Softening - In water softening, hydrated lime is used to remove carbonate hardness from the water. Hardness caused by other calcium and magnesium salts, called noncarbonate hardness, is generally treated by means of the lime-soda process, which entails the precipitation of magnesium by lime. The co-produced calcium salt reacts with the soda ash to form a calcium carbonate precipitate. Lime enhanced softening can also be used to remove arsenic from water. Recent changes to the national drinking water standard for arsenic have increased the need for this treatment.
pH Adjustment/Coagulation - Hydrated lime is widely used to adjust the pH of water to prepare it for further treatment. Lime is also used to combat "red water" by neutralizing the acid water, thereby reducing corrosion of pipes and mains from acid waters. The corrosive waters contain excessive amounts of carbon dioxide. Lime precipitates the CO2 to form calcium carbonate, which provides a protective coating on the inside of water mains.
Lime is used in conjunction with alum or iron salts for coagulating suspended solids incident to the removal of turbidity from "raw" water. It serves to maintain the proper pH for most satisfactory coagulation conditions. In some water treatment plants, alum sludge is treated with lime to facilitate sludge thickening on pressure filters.
Effect on Pathogen Growth - By raising the pH of water to 10.5-11 through the addition of lime and retaining the water in contact with lime for 24-72 hours, lime controls the environment required for the growth of bacteria and certain viruses. This application of lime is utilized where "phenolic water" exists, because chlorine treatment tends to produce unpalatable water due to the phenol present. This process, called "excess alkalinity treatment," also removes most heavy metals.
Removal of Impurities - One of the most common methods of removing silica from water is the use of dolomitic lime. The magnesium component of this lime is the active constituent in silica removal. Lime is also used to remove manganese, fluoride, organic tannins and iron from water supplies.
Typically purchases are made for a 12 month period. Some municipalities such as Chicago contract for as long as five years to minimize cost. Bids are generally open to any bidder who can qualify. There are specific requirements as to method of packaging e.g. bags vs. truckloads. There are also specifications as to whether the chemicals are to be furnished in a dry or liquid form. Specifications can be very specific. For example, granular activated carbon specifications can limit the origin e.g. lignite or bituminous coal, the particle size and other characteristics.
The small utilities may only spend a few thousand dollars per year for a particular chemical, but the large utilities can spend millions of dollars. Canadian plants purchase approximately 10 percent of the total with plants in the U.S. purchasing the remainder.
For more information on North American Public Water Plants and People, click on: http://www.mcilvainecompany.com/brochures/water.html#67ei.
Conferences:
AWWA Pump and Valve Exhibitors
|
ACE11 is the American Water Works Association’s 130th Annual Conference & Exposition, June 12-16, 2011, in Washington, D.C. It’s the water community’s forum to tackle a growing number of challenges, from infrastructure management to water resources protection to advanced treatment technologies. |
|
||||||||||
|
Application Sequencing
Company |
|
||||||||||
|
· A. Y. McDonald Mfg. · A.R.I. USA, Inc. · American Cast Iron Pipe · Badger Meter · Bermad · Cla-Val · Crispin-Multiplex Manufacturing · Danfoss Flomatic · Dezurik · Emerson Process Management · Fluid Metering · GE Water & Process Technologies · Gemu Valves · GF Piping Systems · Grundfos Pumps · Henry Pratt · ITT Corporation · J & S Valve · McWane · Milliken Valve · Milton Roy · Mueller Water Products · National Pump · Neptune Chemical Pump · OCV Control Valves · Parker Hannifin · Pentair Water · Plast-O-Matic Valves · ProMinent Fluid Controls · Red Valve · RF Technologies, Inc. · Rodney Hunt · Ross Valve Mfg. · Siemens Water Technologies · Singer Valve, Inc. · SPX · Tideflex Technologies · VAG Armaturen · Val-Matic Valves & Mfg. Corporation · Verder GPM, Inc. · Watson-Marlow Pumps Group |
|||||||||||
Only a Few Treatment Chemical Exhibitors
Despite the large size of the market for treatment chemicals for drinking water plants, only a few treatment chemical suppliers are going to exhibit.
Arch Chemicals, Inc.
Booth # 2627
Arch produces calcium hypochlorite chlorinators with no requirement for large storage tanks. Arch’s Spray Technology Chlorinators provides efficient alternatives to chlorine gas & liquid bleach.
Calgon Carbon Corporation
Booth # 2537
Calgon Carbon is a global manufacturer/supplier of activated carbons, innovative UV treatment systems, plus value-added services for purification of drinking water, treatment of municipal/industrial wastewater and control of odors.
GAC Chemical Corporation
Booth # 114
GAC Chemical Corporation manufactures ammonium sulfate, an NSF certified source of nitrogen used in the
formation of monochloramine.
Carbon Activated Corporation
Booth # 1459
The company supplier and full service company of Activated Carbon specializing in Coconut Shell & Coal Base Activated Carbon, Change-out Services and Filter Systems for Air & Water Purification, Kidney Dialysis, and Precious Metal Recovery.
Carmeuse Industrial Sands
Booth # 200
Filtration media for water and wastewater treatment systems; gravel pack for water well completions.
Carus Corporation
Booth # 2423
For 90 yrs. the company has supplied permanganates with CARIOX(r) potassium permanganate & CARUSOL(r) liquid permanganate for Fe/Mn, T&O, DBPs, Radium, & other water treatment issues. AQUA MAG(r), VIRCHEM(r), & TPC(r) products for corrosion control & sequestration.
GE Water & Process Technologies
Booth # 2001
GE Water & Process Technologies is a global supplier of water treatment system solutions, including membranes, EDR, analytical instruments, packaged plants, and ancillary equipment. The corporation is also a major water treatment chemicals supplier.
Kemira Water Solutions Inc.
Booth # 2149
Kemira Water, manufacture & supplies a spectrum of inorganic coagulants, Aluminum Sulfate to Ferric Sulfate, Polyaluminum Chloride to Ferric Chloride. Coast to coast manufacturing, supply and technical support is available.
McIlvaine has conducted an InterWEBview™ with Kemira regarding their products:
|
InterWEBview: |
Eka Chemicals
Booth # 508
Eka Chemicals' chlorine Dioxide Technology Purate is claimed to be a safe, economical solution for water treatment needs. Applications include drinking water disinfection, metals reduction, effluent and cooling water treatment and many more.
Lots of Good Presentations
TUE 11
- Water Reuse Lessons Learned - The Evolution of Reuse and Treatment
Technologies
Moderator: Alan Rimer, Black & Veatch
This session takes an in-depth look at the growth of reuse and treatment
technologies. The papers range from the evolution of reuse in Florida to
various case studies related to the treatment of reclaimed water in small and
large projects.
.01 9:00
a.m.
The Evolution of Water Reuse in Florida: Lessons Learned
(PA) Jo Jackson, Brown and Caldwell;
.02 9:30
a.m.
South Florida’s Blueprint for the Implementing of An Advanced Recycled
Water Facility
(PA)
R. Chalmers, CDM
James Ferguson
Layla Llewelyn
.03 10:00
a.m.
Using Design Build to Create the Next Generation of Water Reuse Facility
(PA)
Kelly Comstock, Brown and Caldwell
Kun Suwanarpa
O.P. Shukla
Rod Pope
Ray Williams
.04 10:30
a.m.
Water Reuse in the Oil Sands Region of Canada
(PA)
Alan Rimer, Black & Veatch
Ed Kobylinski
Hans Wolf
.05 11:00
a.m.
Indirect Potable Reuse: Examining the Sustainability of Three Different
Advanced Water Treatment Schemes
(PA)
Jim Lozier, CH2M Hill
Lawrence Schimmoller
Robert Bergman
Jason Curl
.06 11:30
a.m.
Ecological, Decentralized Wastewater Treatment and Reuse Systems: A New
Approach to Manage Growing Demand, Aging Infrastructure
(PA) Will Kirksey, Worrell Water Technologies
TUE 30
- Membrane Processes: From Pre-Treatment to Innovative Applications
Moderator: Robert Bergman CH2M HILL
Seawater pre-treatment, brackish water treatment planning and design,
ultrafiltration retrofit, and gas permeable membranes to remove VOCs.
.01 2:00
p.m.
Application of a Rapid Saltwater AOC Test to Determine Pretreatment
Configuration Impacts on Biofouling in R/O Desalination
(PA) Lauren Weinrich, American Water;
.02 2:30
p.m.
Pretreatment for SWRO - Current Practices and Future Trend
(PA)
Srinivas Veerapaneni, Black & Veatch
Benjamin Klayman
Sunny Wang
.03 3:00
p.m.
Process Design and Cost Optimization of a Hybrid: Seawater – Brackish RO
Desalination System in Oceanside, California
(PA)
Mark Wilf, Tetra Tech
Howard Arnold
Brad Nguyen
Steven Tedesco
.04 3:30
p.m.
Desalination Pilot Study: Effects of Extended Operation and Air Leaks on
a Brackish Groundwater in Texas
(PA)
Justin Sutherland, Carollo Engineers
Graham Juby
William Causey
Lance Rothe
Duane Bryant
Kevin Morrison
.05 4:00
PM
6 Years Later: A Look Back at the First Zeeweed 1000 Membrane WTP
Retrofit in the United States
(PA)
Clint Dilley, Epic Engineering
David Gardner
Don Olsen
Jerry Nielson
James Peterson
.06 4:30
p.m.
Innovative Use of Gas Permeable Membranes to Remove Entrained Air, VOCs
and Radon from Groundwater
(PA)
Robert Raczko, United Water
John Dyksen
Christopher Savino
TUE
19 - Integrating Membrane Filtration into Existing Water Treatment Plants
Moderator: Mark White CDM, Inc.
This session provides an overview of the key planning, procurement, design,
construction, and startup issues associated with integrating membrane filtration
systems into existing operating plants. Case studies provide valuable utility
perspective.
.01 2:00
p.m.
Planning, Procurement and Design of Membrane Filtration Systems
(PA)
Ian Crossley, Hazen & Sawyer PC
Kristen Barrett
Anni Luck
.02 2:30
p.m.
Construction and Commissioning of Membrane Filtration Systems
(PA) Jesus Garcia-Aleman, CH2M HILL Canada
.03 3:00
p.m.
Startup and Operations for Membrane Filtration Systems
(PA) Karla Kinser, MWH Americas
.04 3:30
p.m.
Membrane Manufacturer Perspective of the Implementation Process
(PA)
Thomas Lebeau, Siemens Water Technologies Corp.
(PA)
Steve Watzeck, GE Water & Process Technologies
.05 4:00
p.m.
Converting a 10 MGD Filter Building into a 40 mgd Submerged Membrane
System at Manitowoc, WI
(PA) Robert Michaelson, Manitowoc Public Utilities
.06 4:30
p.m.
Implementing Advanced Drinking Water Treatment in Multiple Facilities at
the Region of Peel
(PA) Andrew Farr, Reg. Municipality of Peel Public Works
Global Orchard Provides Continuing Calendar of Water Conferences
Here are some of the water related conferences which are scheduled in the next 5 months. For the complete calendar, click on:
See the Global Orchard coverage of the other presentations under EVENTS at:
Free News and InterWEBviews ™
http://www.mcilvainecompany.com/Decision_Tree/subscriber/Tree/Default.htm.
|
11/13/2011 |
International Water Conference 2011 |
|
|
10/26/2011 |
Cleanroom Technology 2011 |
|
|
10/17/2011 |
WEFTEC 2011 |
|
|
7/18/2011 |
AMTA / SEDA 2011 Joint Conference & Exposition |
|
|
7/4/2011 |
Singapore Water Week Expo |
|
|
6/12/2011 |
AWWA ACE 2011 |
--------------------
Calgon Carbon Sponsors Free Sessions on Safe Water
Calgon Carbon Corporation (NYSE: CCC) today announced the 2011 dates and locations for its popular municipal drinking water technical seminar, “Water Made Better.” Calgon Carbon will conduct this seminar in nine cities in North America from May to December. This free program is designed to educate municipal officials and water and wastewater professionals on solutions available to make water safer and cleaner. The 2011 seminar series features revised and expanded versions of the presentations first introduced in 2009, reflecting the latest technological and market developments for municipalities.
Specialists in activated carbon and ultraviolet (UV) technology will lead the seminars. Attendees will learn about granular activated carbon (GAC), custom reactivated GAC, and space-saving, pre-engineered adsorption equipment to help water utilities comply with the Environmental Protection Agency’s Stage 2 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule. Calgon Carbon will also present information about contaminants of emerging concern, and the solutions to address these tough challenges.
A detailed overview of UV
technology![]() and the latest information about UV disinfection and UV Oxidation for drinking
water, wastewater and reuse applications will be provided. Additionally, Calgon
Carbon will review how GAC and UV can work together to address taste and odor
concerns in drinking water.
and the latest information about UV disinfection and UV Oxidation for drinking
water, wastewater and reuse applications will be provided. Additionally, Calgon
Carbon will review how GAC and UV can work together to address taste and odor
concerns in drinking water.
Calgon Carbon’s technical seminars will be conducted in the following cities during 2011 (operator credits will be provided by individual states, pending approval):
· Birmingham, AL – Thursday, May 5
· Toledo, OH – Thursday, May 12
· Denver, CO – Thursday, June 23
· Las Vegas, NV – Tuesday, August 30
· Vancouver, BC – Wednesday, August 31
· Raleigh, NC – Thursday, September 15
· St. Louis, MO – Tuesday, October 11
· Ottawa, ON – Thursday, November 3
· Dallas, TX – Thursday, December 15
Each seminar, free to registered attendees, is scheduled from 7:30 a.m. to 3:15 p.m., with a continental breakfast and lunch provided by Calgon Carbon. For registration information, visit www.calgoncarbon.com.
--------------------
Water Product Updates
Here are the project update headlines in recent weeks appearing in the McIlvaine North American Public Water Plants and People. More information on this service is found at: http://www.mcilvainecompany.com/brochures/water.html#67ei
Federal
USDA Rural Development Announces Projects to Improve Water Quality and Benefit Rural Residents
ALABAMA
Florence Considers 2 Water Projects
CALIFORNIA
Sacramento Plans $150 Million Water Plant Upgrades
Anaheim to Build Municipal Water Reuse System
COLORADO
Eagle Needs New Water Plant
FLORIDA
Davenport Plans $4.9 Million Wastewater Project
Cocoa Opts Out of Water Treatment Plant Project
MASSACHUSETTS
Newburyport Planning $9 Million Water Plant
MINNESOTA
East Bethel Decides on Water Plant
NEW YORK
Construction to Begin on Newburgh Water Treatment Plant
NEW JERSEY
Alpha Borough Plans $2.2 Million Water Project
NEW YORK
Aurelius, Cayuga Plan $10 Million Wastewater/Drinking Water Projects
NORTH DAKOTA
Williston Considers Pipeline, Water Plant Expansion
OHIO
Marietta Moves Forward on $22 Million Wastewater Treatment Project
PENNSYLVANIA
Penn Project Cost Soars by $1 Million
Gov. Corbett Announces $134 Million Investment in Water Infrastructure Projects in 21 Counties
Cheswick Needs New Water Treatment Plant
SOUTH DAKOTA
Rapid City to Rebid Water Treatment Plant
TEXAS
Sugar Land Breaks Ground for New $69 Million Water Treatment Plant
CANADA
Saskatoon’s Water Plant to Be Replaced
Prince Albert Begins Phase 2 Water Plant Upgrade
Abbottsford Considers New $300 Million Water Treatment Centre
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ARIZONA
$8.8 Million for Gilbert Water Project
ARKANSAS
$16 Million for New Ozark Mountain Water Plant
CALIFORNIA
$320 Million for San Francisco Area Water Project
Modesto’s New Water Plant Needs Major Reconstruction
FLORIDA
Marco Island Water Project Moves Forward
ILLINOIS
$1.5 Million for New Diamond Water Plant
NEVADA
Yerington Approves 2011 Bond Ordinance for Water Treatment Plant
PENNSYLVANIA
Erie Water Authority approves $9 Million for Water Project
SOUTH DAKOTA
Rapid City Water Treatment Plant Bids under Budget
TEXAS
Austin’s $508 Million Water Plant Project Begins
Voters Approve Funds for Highland-Fernwood Water Treatment Plant
VIRGINIA
Staunton Has Multiple Water Projects
CANADA
$19 Million for New Drayton Valley Water Plant
Houston Plans $4.2 Million Water Treatment Plant
You can register for our free McIlvaine Newsletters at: http://www.mcilvainecompany.com/brochures/Free_Newsletter_Registration_Form.htm
Bob McIlvaine
President
847 784 0012 ext 112
rmcilvaine@mcilvainecompany.com
|
Copyright © 2011 McIlvaine Company. All Rights Reserved Ph: 847-784-0012 | Fax; 847-784-0061 Click here to un-subscribe from this mailing list |